The knee joint is a hinge joint between the femur, the tibia, and the patella. The balance of the joint is provided by static and dynamic structures. These structures consist of capsules and ligaments, muscles and tendons. The knee joint that carries the whole load of the body is essential for the range of movement. The muscles in the knee joint have a certain strength and must be balanced. Some problems in the joint may occur as a result of overloading the knee, sporting activities, and age-related knee wear.
As the knee joint plays a major role in walking, sitting and standing, bending and straightening, it is exposed to traumas. Arthroscopic surgery is used in most of the knee problems due to the variety and pathologies of the knee joint.
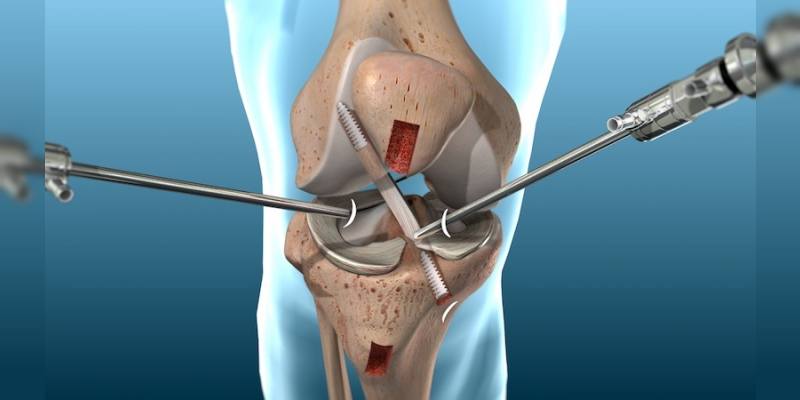
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical method. It is also referred to as closed surgery because it is performed through very small holes. It provides diagnosis and treatment by inserting camera and ancillary devices through holes of approximately 0.5 cm. The surgeon inserts repair tools through one hole and the camera and light mean through the other hole. The surgeon watches area on the high-resolution display and the treatment is carried out. The camera system can see every detail thanks to its high resolution and multiple zoom possibilities. Therefore, it provides confidence and comfort during surgery.
Knee arthroscopy has advantages in the postoperative period as well as during surgery. Its biggest advantage is that it allows the patient to recover faster and to feel less pain than open surgery. Having 0.5 cm holes instead of 10-15 cm incisions as with open surgery directly affects the healing process. Today, knee arthroscopy is preferred in the treatment of many knee problems. Especially in meniscus and ligament injuries, open surgery is almost completely discontinued.
In Which Diseases Is Knee Arthroscopy Applied?
- Meniscus tear
- Anterior cruciate ligament injury
- Lateral ligament injuries
- Osteoarthritis of knee
- Cartilage lesions
- Synovitis
- Intraarticular free body
Meniscus Tear
As the joint between the femur and the tibia does not fully overlap, the meniscus provides compliance between them. Each knee has two menisci as internal and external. The meniscus is involved in spreading the load over a larger area and protecting the joint cartilage from high pressure. It is a kind of suspension of the knees. Wear and tear of the meniscus may occur as a result of deformation or trauma with advancing age. A sudden stop, rotation, forced bending of the knee and direct contact may result in injury or tears. In contact sports such as basketball and football, such injuries are very common. Arthroscopic (closed) surgical method is often preferred instead of open surgical treatments for meniscus problems. The incisions made for arthroscopy are very small. With the devices inserted through these small incisions, intra-articular imaging is performed and meniscus injuries or tears are treated. In contrast to open surgery, arthroscopy provides greater convenience since it can be visualized anywhere in the joint.
Ligament Injuries
Knee ligaments are structures that allow the knee to move in harmony with one another. There are two most vulnerable ties. These are the front cross-link in the middle of the knee and the inner side in the knee. Injuries here cause loss of strength in the knee and severe pain. Other problems may occur if they are not treated. Knee arthroscopy is the most preferred method in ligament treatments. With this method, treatment is performed by imaging and intervention from minimal incisions in the joint.
Advantages of Knee Arthroscopy when compared to Open Surgery
The most important advantage of knee arthroscopy is making small incisions. This results in a comfortable and quick recovery process. This is the difference between open surgery and this method. While in open method, 10-15 cm incisions are made, and arthroscopy is performed with 0.5 cm holes. The smaller the incision, the shorter the healing process. In addition, the possibility of mistakes decreases considerably with the applied imaging technique. The images taken with the help of the fiberoptic instruments allow the physician to work more easily and easily see everywhere in the joint. In fact, knee problems that cannot be seen during the preoperative examination can be detected during arthroscopy and treated in the same session. Although large incisions are made to reach the joint in open surgeries, it is not possible to see the entire joint.
The instruments used in arthroscopic surgery are completely specific to arthroscopy. Since the thickness of the instruments used to examine the areas and structures within the joint and repair the diseased or injured structures is small millimeters, the operation can be performed with small incisions. There is less pain than open surgery. Small incisions are almost lost a few months after surgery. Postoperative rehabilitation is short and easy. The patient may return to daily activities, work, and sports early.
What to pay attention After Knee Arthroscopy
In the first week after surgery, cold treatment is required to reduce edema and pain in the area. With this application, the edema will be reduced and the exercises to be done will be easier. Exercising regularly increases blood circulation and prevents blood clotting, accelerating healing. The necessary instructions should be followed regularly by using the medications prescribed by the doctor.